缓存 AI 规划和定位
Midscene 支持缓存 Plan 的步骤与匹配到的元素位置信息,减少 AI 模型的调用次数,从而大幅提升执行效率。请注意,DOM 元素缓存仅在 Web 自动化任务中支持,且存在一定局限性。
效果
当缓存命中时,脚本的执行时间会显著降低。例如在如下案例中,执行耗时从51秒降低到了28秒。
- before
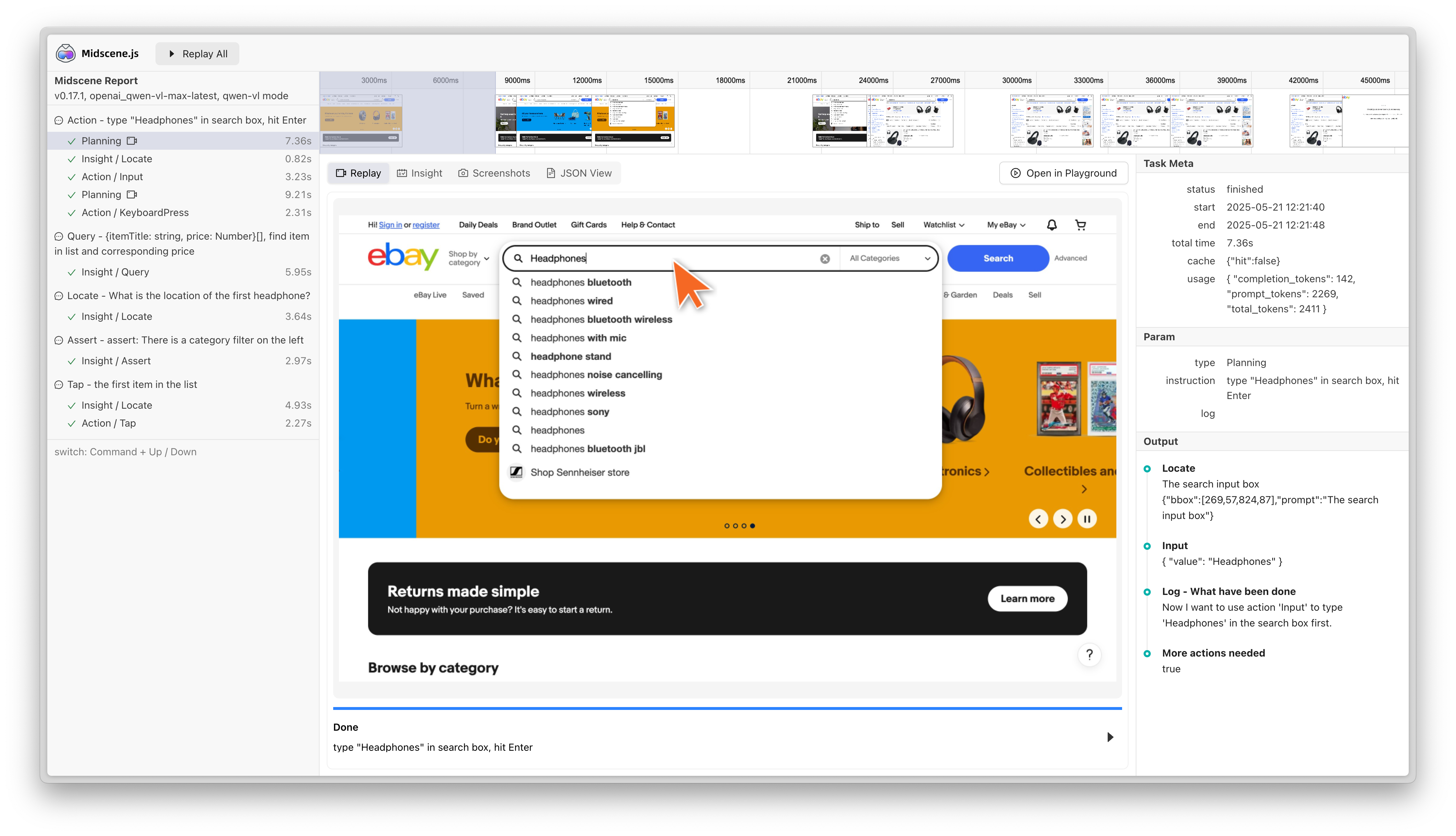
- after
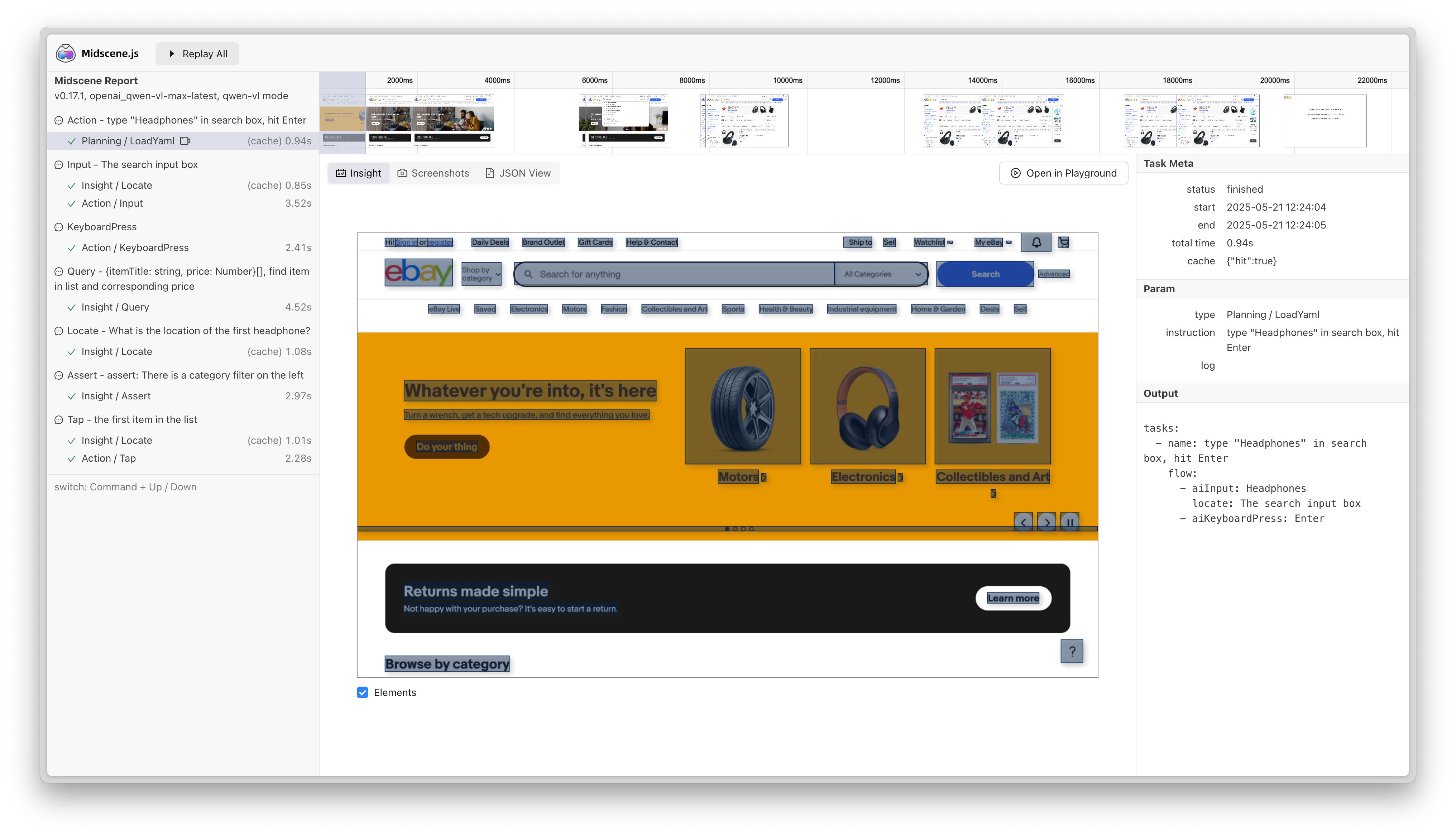
缓存文件和存储
Midscene 的缓存机制基于输入的稳定性和输出的可复用性。当相同的任务指令在相似的页面环境下重复执行时,Midscene 会优先使用已缓存的结果,避免重复调用 AI 模型,�从而显著提升执行效率。
缓存的核心机制包括:
- 任务指令缓存:对于规划类操作(如
ai、aiAct),Midscene 会将 prompt 指令作为缓存键,存储 AI 返回的执行计划 - 元素定位缓存:对于定位类操作(如
aiLocate、aiTap),系统会将定位 prompt 作为缓存键,存储元素的 XPath 信息,下次执行时先验证 XPath 是否仍然有效 - 失效机制:当缓存失效时,系统会自动回退到 AI 模型重新分析
- 永不缓存查询结果:查询类操作(如
aiBoolean、aiQuery、aiAssert)不会被缓存
缓存内容会保存到 ./midscene_run/cache 目录下,以 .cache.yaml 为扩展名。
如果缓存未命中,Midscene 将会重新调用 AI 模型,并更新缓存文件。
缓存策略
通过配置 cache 选项,你可以为 Agent 启用缓存。
禁用缓存
配置方式:cache: false 或不配置 cache 选项
完全禁用缓存功能,每次都重新调用 AI 模型。适合需要实时结果或调试时使用。默认情况下,如果不配置 cache 选项,缓存是禁用状态。
读写模式
配置方式:cache: { id: "my-cache-id" } 或 cache: { strategy: "read-write", id: "my-cache-id" }
自动读取已有缓存,执行过程中自动更新缓存文件。strategy 的默认值是 read-write。
YAML 模式还支持配置 cache: true,自动使用文件名作为 cache ID。
只读,手动写入
配置方式:cache: { strategy: "read-only", id: "my-cache-id" }
只读取缓存,不自动写入缓存文件,需要手动调用 agent.flushCache() 写入缓存文件,适合生产环境,确保缓存的一致性
只写模式
配置方式:cache: { strategy: "write-only", id: "my-cache-id" }
只写入缓存,不读取已有缓存内容。每次执行时都会调用 AI 模型,并将结果写入缓存文件。适合初次建立缓存或更新缓存时使用。
兼容方式(不推荐)
通过环境变量 MIDSCENE_CACHE=1 配合 cacheId 配置,等同于读写模式。
使用 Midscene 的 Playwright AI Fixture
在使用 @midscene/web/playwright 中的 PlaywrightAiFixture 时,可以��通过相同的 cache 配置来管理缓存行为。
禁用缓存
读写模式
只读,手动写入
在只读模式下,需要在测试步骤完成后手动将缓存写入文件。可以通过 fixture 提供的 agentForPage 方法获取底层 agent,然后在需要持久化的时刻调用 agent.flushCache():
只写模式
在只写模式下,每次测试都会调用 AI 模型,并将结果自动写入缓存文件,不会读取已有缓存。
缓存清理
Midscene 支持在写入缓存时清理未使用的缓存记录,确保缓存文件保持精简。这个功能是完全手动的,需要显式调用 agent.flushCache({ cleanUnused: true })。
手动清理机制
当调用 agent.flushCache({ cleanUnused: true }) 时,系统会:
- 保留使用过的缓存:本次运行中被匹配和使用的缓存记录会被保留
- 保留新增的缓存:本次运行中新生成的缓存记录会被保留
- 删除未使用的缓存:旧的、未被使用的缓存记录会被自动删除
- 写入文件:清理后的缓存会被写入��文件
使用方式
在测试的 afterEach 中统一调用:
Playwright AI Fixture 用户:
清理行为说明
- read-write 模式:调用
flushCache({ cleanUnused: true })会清理并写入文件 - read-only 模式:调用
flushCache({ cleanUnused: true })也会清理并写入文件(手动 flush 覆盖 read-only 限制) - write-only 模式:不执行清理(因为不读取缓存)
注意:如果不传 cleanUnused: true 参数,flushCache() 只会写入文件而不会清理未使用的缓存。
FAQ
没有生成缓存文件
请确认你已正确配置缓存:
- �直接创建 Agent: 在构造函数中设置
cache: { id: "your-cache-id" } - Playwright AI Fixture 模式: 在 fixture 配置中设置
cache: true或cache: { id: "your-cache-id" } - YAML 脚本模式: 在 YAML 文件中设置
agent.cache.id - 只读模式: 确保调用了
agent.flushCache()方法 - 旧方式: 设置了
cacheId并启用了MIDSCENE_CACHE=1环境变量
如何检查缓存是否命中?
你可以查看报告文件。如果缓存命中,你将看到 cache 提示,并且执行时间大幅降低。
为什么在 CI 中无法命中缓存?
你需要在 CI 中将缓存文件提交到仓库中,并再次检查缓存命中的条件。
如果有了缓存,是否就不需要 AI 服务了?
不是的。
缓存是加速脚本执行的手段,但它不是确保脚本长期稳定执行的工具。我们注意到,当页面发生变化时,缓存可能会失效(例如当元素 DOM 结构发生变化时)。在缓存失效时,Midscene 仍然需要调用 AI 服务来重新执行任务。
如何手动删除缓存?
你可以删除 ./midscene_run/cache 目录中的缓存文件,或者编辑缓存文件的内容。
如果我想禁用单个 API 的缓存,怎么办?
你可以使用 cacheable 选项来禁用单个 API 的缓存。
具体用法请参考对应 API 的文档。
使用 XPath 缓存元素定位信息的局限性
Midscene 使用 XPath 来缓存元素定位信息。我们使用相对严格的策略来防止误匹配。在以下情况下,缓存不会命中:
- 新元素在相同的 XPath 下的文本内容与缓存元素不同。
- 页面的 DOM 结构与缓存时的结构不同。
此外,由于元素定位缓存依赖 DOM 结构,以下场景无法使用缓存功能:
- Canvas 元素:Canvas 内部的图形内容不存在 DOM 节点,无法通过 XPath 定位。
- 跨域 iframe:浏览器安全策略限制了对跨域 iframe 内部 DOM 的访问。
- Shadow DOM(closed 模式):封闭的 Shadow DOM 无法从外部访问其内部结构。
- WebGL / SVG 动态内容:动态生成的图形内容可能没有稳定的 DOM 结构。
当缓存未命中或不可用时,Midscene 将回退到使用 AI 服务来查找元素。
获取缓存相关的调试日志
在环境变量中配置 DEBUG=midscene:cache:*,你可以看到缓存相关的调试日志。

